Understanding Congenital Anomalies:
These problems arise in babies during pregnancy and are known as anomalies or malformations. There are around 4000 different varieties of these abnormalities, which are split into two categories:
-
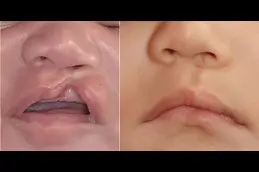
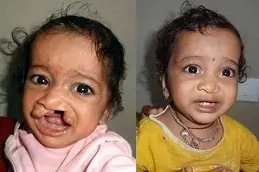
Structural: When a child is born without or with a deformity in a portion of the body. Cleft palate, club foot, and spina bifida are the most prevalent conditions in this category.
-
Functional: These are abnormalities in which the chemical composition of the neurological, metabolic, or immunological systems of the body is disrupted. Down syndrome, deafness, and blindness are some of the most frequent.
Which specialist to see?
The gynecologist who oversees pregnancy is the expert in spotting congenital defects. The pediatric surgeon will be the specialist in charge of monitoring and evaluating the kid after birth, while the pediatrician will be in charge of treating specific anomalies.
Malformations may also be treated by other professionals such as speech therapists or psychologists.
Results:
The abnormalities do not have a definitive remedy. However, youngsters are frequently treated to prevent subsequent issues. Your child’s treatment will be determined by his or her symptoms, age, and overall health. It will also be determined by the severity of the problem.
Types:
There are thousands of abnormalities and defects. Following are some of the types:
Hand Deformities:
The hand, when anatomically full and working properly, constitutes an essential component for proper life function in humans. The contact between two fingers, the loss or addition of one or two fingers, and digit deformation are some of the most prevalent occurrences.
Cloacal Anomaly:
It’s a rectum, vaginal, and urethral deformity all rolled into one. Amongst the most serious technical issues in pediatric surgery is this deformity.
Polysplenia:
The Accessory Spleen, also known as the Accessory Spleen, is a developmental anomaly that occurs before birth and is one of the most prevalent malformations. It is seen in the spleen ligaments and, less commonly, in the pancreas.
Renal Anomalies:
Kidney abnormalities are structural alterations in the kidneys that remain beyond the normal range, resulting in compromised renal function.
Heart Disease:
Cardiac valve disorders are one of the most frequent heart ailments. If the valve apparatus, cardiac septa, walls, or major veins radiating from the heart are damaged in any manner, blood flow might be disrupted.
Causes:
The origin of most of these malformations is unknown, but several agents have been identified that may be related to their appearance of them:
These anomalies can be passed down through the generations from parents who have their own oddities or carry genes that cause these disorders. However, many are caused by non-inherited new chromosomal abnormalities or gene mutations that emerge in the kid.
The development of a healthy fetus necessitates a healthy diet. A shortage of vitamin B9 in the diet raises the risk of spina bifida or cleft palate in the baby.
A birth defect can be caused by some illnesses. The age of the fetus at the time of exposure determines whether the condition causes a congenital impairment.
Radiation, medicines, and poisons are all harmful substances that can cause or raise the risk of congenital impairment. When, how much, and how long the pregnant woman was exposed to dangerous substances determines whether or not a congenital impairment occurs.
Can they be Prevented?
Several basic preventative methods for abnormalities are recommended by gynecology doctors and health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO):
- During pregnancy, pay close attention to a pregnant mother’s food since she will need to offer the vital vitamins and minerals, such as folic acid.
- Tobacco and alcohol are two hazardous or damaging drugs to avoid.
- Make sure your diabetes is under control if you have it.
- Toxic or harmful compounds, such as insecticides, should be avoided.
- Radiation and medicines should be avoided.
- Boost immunization efforts, particularly against the rubella virus.
Diagnosis:
Different methods of diagnosis are available both before and after birth. Ultrasound, blood testing, and chorionic villus sample can all be used to diagnose problems prior to delivery. Physical examinations or blood tests can be performed after birth.
Before giving Birth:
Doctors decide whether a woman’s chances of having a kid with abnormalities are raised. Women with the following risk factors have a higher chance:
- Age of the Elderly
- Miscarriages have been a problem in the past.
- Other children have abnormalities, and some children have died for unknown reasons.
To see if the fetus has any problems, a fetal ultrasound or MRI is performed. Blood testing can sometimes aid in the detection of flaws. High amounts of alpha-fetoprotein in a mother’s blood, for example, could suggest a problem with the brain, spinal cord, or other organs.
After Birth:
A child’s physiological examination is performed by doctors. During this examination, the doctor looks at the newborn’s skin, head and neck, heart and lungs, belly, and genitals. Some neonates have a physical appearance that indicates a specific disease.
Treatment Options:
Many deformities can be fixed or improved with pediatric surgery, even during pregnancy. In some circumstances, neonates may require medication from the moment they are born, or possibly emergency surgery to save their lives.
The treatment required for each patient varies depending on the deformity or pathology as well as the course of the disease. The following are some of the most common treatments:
Surgical Treatment:
Some changes are limited to a single organ and can be corrected surgically with relatively simple and well-established methods. These, on the other hand, are more complicated diseases that affect the eye, appendages, cleft lip, and other organs.
The type of surgery required depends on the circumstances, and a combination of procedures may be required to achieve the desired results.
Gene Therapy:
The gene that is absent or faulty is replaced in this procedure. Its goal is to correct or replace a mutant gene, inhibit a mutated gene that is causing the problem, or inject a normally functional copy of the gene into cells to assist the body in producing a complete protein.
Enzyme Replacement Therapy:
Enzyme replacement therapy, often known as ERT, is a promising experimental treatment for a number of hereditary illnesses. It entails receiving an intravenous infusion of an enzyme that the body does not make, as well as weekly visits to the hospital for information.
Prenatal Treatment:
Not only can problems be diagnosed before birth, but they can also be treated with prenatal treatment. Urinary tract obstruction and uncommon lung tumors are two disorders that can be addressed.
Congenital Anomalies Treatment In Georgia (FAQS):
Can Congenital Anomalies Be Treated?
To receive a personalized response regarding this, the patient needs to sign up for consultation, still, yes they are capable of being cured. Depending upon the intensity of the health issue the patients are suggested to either pursue the surgical, non-surgical, or any other customized course of action.
When Is The Most Common Time For Congenital Anomalies To Occur?
To be precise, the patients can commence bearing with this health hazard when the minimalistic human individual is only three months, old and still going through the development of the organs.
How Will You Prevent Congenital Anomalies?
On a friendly note, the patient needs to consult the specialist in order to receive a personalized response regarding this. However, the patients can be prevented from the severe consequences of congenital anomalies with the help of vaccines, personalized consumption of folic acid or iodine, or any other customized course of action.
How Long Is The Life Expectancy Of Congenital Anomalies?
The life expectancy of congenital anomalies relies upon the personalized health condition of the patient, along with the customized curing sessions they have been attending.
Does Maternal Age Affect Congenital Anomalies?
According to the researchers yes it has been one of the factors which have manipulated and affected the congenital anomalies.
What Is The Higher Risk Of Congenital Anomalies?
A few of the major factors that have been involved in the eruption of congenital anomalies are maternal age, genetic factors, environment, maternal condition, and the overall atmosphere of the patient.
What Is The Importance Of Congenital Anomalies?
The patients need to get rid of this health hazard because later it is capable of causing any type of disability suffered by the patients like developmental, intellectual, or physical disability.
What Is The Mortality Rate For Congenital Anomalies?
The mortality rate for congenital anomalies varies from region to region. So, it can not be extracted from a generalistic stance, still, with the help of a customized course of action the patients are mostly expected to cure the health hazard.
Book an Appointment!
If you are looking for Congenital anomalies treatment in Georgia
, Tbilisi contact experts at Sydney Royal Clinic by filling out the consultation form below to book an appointment right away.